
News
What is a Modular Space House and How Does It Work?
The Modular Space House represents a transformative approach in the housing industry. According to the National Association of Home Builders, modular homes utilize about 20-30% less energy than traditional houses. This reduction not only benefits the environment but also provides cost savings for homeowners. Experts like Dr. Emily Larson, a leader in modular construction, emphasize the potential of these homes: "Modular Space Houses redefine efficiency and livability in urban environments."
Modular Space Houses are assembled in sections to create functional, adaptable living spaces. This building method accelerates construction while maintaining quality. Each module is constructed in a controlled environment, minimizing waste. The flexibility of design allows these homes to fit various needs, from single-family to multi-unit dwellings.
Despite their advantages, some challenges exist. Public perception often associates modular homes with lower quality or temporary structures. Changing this mindset requires education about their durability and design potential. Addressing these misconceptions remains crucial for the industry's growth. The evolution of the Modular Space House continues, reflecting a need for innovation in housing solutions.

What Is a Modular Space House? An Overview of Its Definition
A modular space house is an innovative construction method. It utilizes prefabricated sections to create livable spaces. These sections, or modules, are crafted off-site. Once completed, they are transported to the desired location. This approach reduces construction time significantly. According to the Modular Building Institute, modular homes can be built 30-50% faster than traditional homes.
One key advantage of modular space houses is their sustainability. Data shows that the modular construction process generates less waste compared to traditional building methods. For instance, approximately 90% of construction waste is minimized. This makes modular homes a greener alternative. However, not all designs are feasible with modular construction. The aesthetic choices might feel limited at times. Additional customization options can lead to higher costs, which can deter some potential buyers.
Modules can be stacked or arranged in various configurations. This flexibility allows homeowners to adapt their space based on needs. It's evident that modular homes are gaining popularity. Reports suggest a growth rate of about 10% annually in the modular housing market. Nonetheless, challenges persist, including logistical issues during transportation. These obstacles highlight the need for further innovation in the field.
What is a Modular Space House and How Does It Work?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A modular space house is a prefabricated structure made from several sections or modules that are constructed off-site and assembled on location. |
| Construction Process | Modules are manufactured in a controlled environment to ensure quality, then transported and assembled on-site. |
| Advantages | Faster construction time, reduced waste, better quality control, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional building methods. |
| Customization | Modular homes can be designed and customized to meet the specific needs and preferences of the owner, including layout, size, and features. |
| Environmental Impact | Modular homes can be built using sustainable materials and construction practices, making them a more environmentally friendly option. |
| Market Trends | The popularity of modular space houses is increasing as more people seek affordable and efficient housing solutions. |
Historical Development of Modular Homes: Key Milestones and Innovations
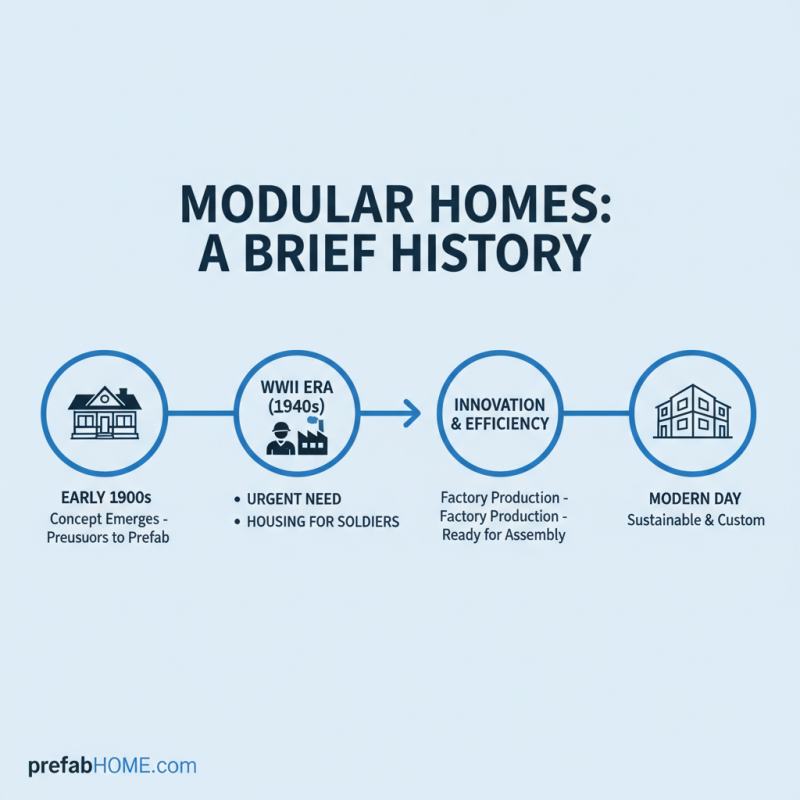
The history of modular homes dates back to the early 20th century. The concept gained traction around World War II. Manufacturers needed efficient housing solutions for soldiers returning home. This urgency led to innovative designs and construction methods. Factories began producing prefabricated sections, ready for assembly.
By the 1960s, modular homes evolved further. The introduction of advanced materials improved durability and efficiency. New techniques allowed for better insulation and energy conservation. Many homeowners appreciated these features, especially during economic downturns. However, the perception of modular homes remained mixed. Some viewed them as temporary solutions, lacking aesthetic appeal.
The late 20th century saw a shift in attitudes. Architects began embracing modular designs. They recognized the potential for modern, stylish homes. Environmental consciousness also influenced this change. Sustainability became crucial. Innovations in energy-efficient technologies emerged. Yet, some challenges remain. The industry still grapples with regulations and zoning laws.
How Modular Space Houses Are Constructed: The Manufacturing Process
Modular space houses are an innovative solution for modern living. They are built in sections, or modules, at a factory. The process starts with designing each module separately. Architects create blueprints for these structures, ensuring that they meet regulations and standards.
Once the designs are finalized, materials are sourced. This includes wood, steel, and insulation. These materials can vary in quality. Some manufacturers use sustainable options, while others do not. After that, workers assemble the modules in a factory. This assembly process can take a few weeks. However, not all factories follow the same quality control measures, which can lead to inconsistencies.
Finally, the completed modules are transported to the building site. Cranes lift and place each piece in its designated spot. This method significantly reduces construction time on site. However, challenges arise in aligning and connecting the modules seamlessly. If not done correctly, gaps can appear, affecting durability and aesthetics. There's a constant need for feedback and improvement in this process. Each project serves as a learning opportunity for future developments.
Advantages of Modular Space Houses: Cost, Efficiency, and Sustainability
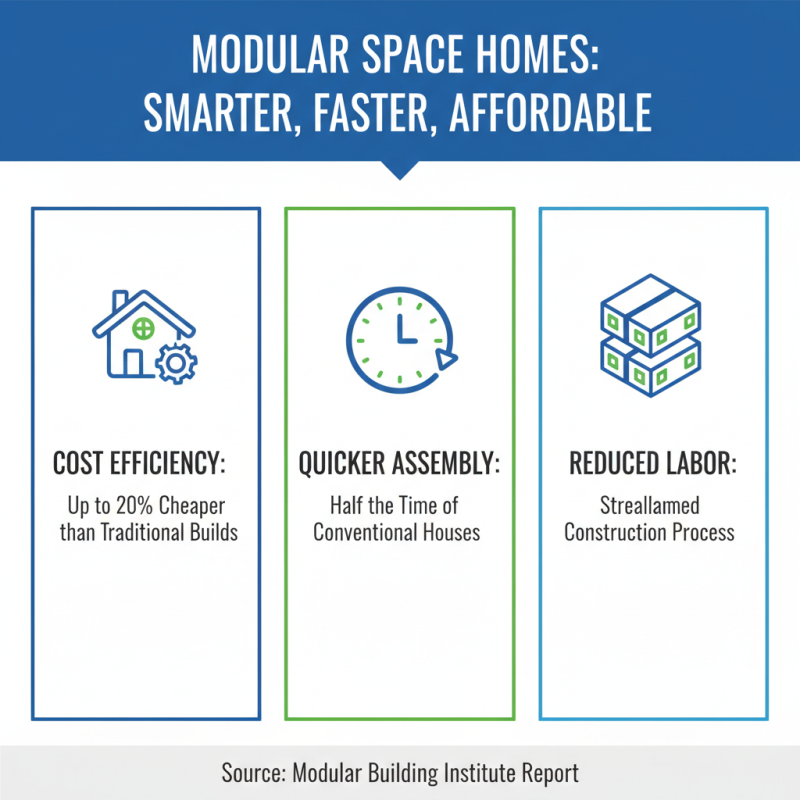
Modular space houses are gaining traction for their cost efficiency. According to a report by the Modular Building Institute, modular construction can be up to 20% cheaper than traditional building methods. This is mainly due to reduced labor costs and quicker build times. In many cases, a modular home can be completed in half the time of a conventional house.
Efficiency is another significant advantage. These homes are built in controlled factory environments, ensuring high-quality construction. A study from the National Institute of Standards and Technology shows that factory-built homes can lead to 30% less waste. It’s a process that not only saves money but also supports sustainable practices.
Sustainability goes beyond waste reduction. Modular homes often utilize eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs. However, the challenge remains in standardization and permitting processes, which can vary by region. While modular homes offer a lot, potential buyers must navigate local regulations. There is still room for improvement in integrating green technologies. Investing in modular homes may sound promising, yet some aspects require careful consideration.
Future Trends in Modular Housing: Market Growth and Technological Advances
Modular housing is gaining traction as a viable solution for modern living. A recent report projects the modular construction market will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth reflects rising demand for affordable housing. Many see modular homes as a response to urban housing challenges.
Technological advancements play a crucial role in this trend. Automation in construction processes reduces time and costs significantly. For instance, prefabricated parts can be assembled on-site in days rather than months. However, imperfections still persist. Some concerns include the durability of materials used and the potential for subpar finishes.
The push for eco-friendly designs is another key factor. A substantial portion of modular homes incorporates energy-efficient features. Yet, the industry isn't perfect. Challenges in obtaining permits and building codes can slow progress. Balancing innovation with regulation remains a persistent issue for stakeholders.
Related Posts
-

5 Reasons Why Tesla Capsule House is the Future of Sustainable Living
-

How to Create Your Dream Home with Modular Space House Solutions
-
Why Choose a Prefabricated House? Benefits and Advantages Explained!
-

Challenges Faced by Homeowners in Adopting the Best Tiny House Capsules
-

Emerging Innovations in Prefab Capsule Houses: Advantages Leading to Sustainable Living by 2025
-

Explore the Future of Living with Innovative Modular Space Capsule Homes
